Visioning the future:
In this workshop we proposed to think about the relationship between work and home-life in the near future, so that the functional aspects of future domestic space and new morphologies could be explored with both proposed criteria of flexibility and comfort. We also worked in how the sociological aspects will affect in the future to the design of the space and furniture. In this workshop was more interesting for us to propose than to resolve or to devise than to formalize. Going out the daily routine we have researched how we will live in one hundred years, an how sociological aspects will affect in the future to the design of the space and furniture.
The workshop developed two virtual possibilities of placement:
- The housing of the future, lonely in the countryside, without connection with the city, so that it will be able to operate independently or grouped with other units sharing certain resources.
- Integration into “smart cities” sharing resources and infrastructures of the future city.
After selecting de place students had to select the strategy to work between any of next suggestions:
- The house grows from the ground in which it will be placed, using the latest technology (3D “printers”) and generating on site the necessary pieces to be built.
- Working with prefab elements: capsules, technical boxes and walls (thick elements which contain the facilities and their connection points with capsules)
- Completely prefabricated spaces which unfold at the destination or can be joined to get a bigger space.
The Invited professors in the week that participated in this workshop were: Prof Natalia Przesmycka (College of Enterprise and Administration in Lublin) Lecture: Modern polish house. Prof Sabine Pollak (Kunstuniversität Linz) Lecture: A manifesto for new collectivities. Prof Dina Suhanova (Faculty of Architecture and Design of the RISEBA in Latvia) Lecture: Soviet modernity in Latvia. Their Lectures were useful to provide concepts. In addition we saw some ideas than helped us for the job.
The cinema and the future of architecture:
Throughout the 20th century, we have had numerous attempts (about design, philosophy, films,) in order to predict how the housing would be in the future. Films like Metropolis in 1927 proposed a vision of the future that was not far from reality. Circulation levels, flying cars crossing the city and abstract forms in the buildings, following the new theories of architecture. In the same way the film “Blade Runner”. used a house designed by Frank Lloyd Wright as a future house. It was the Ennis House designed in 1923 in Los Angeles.
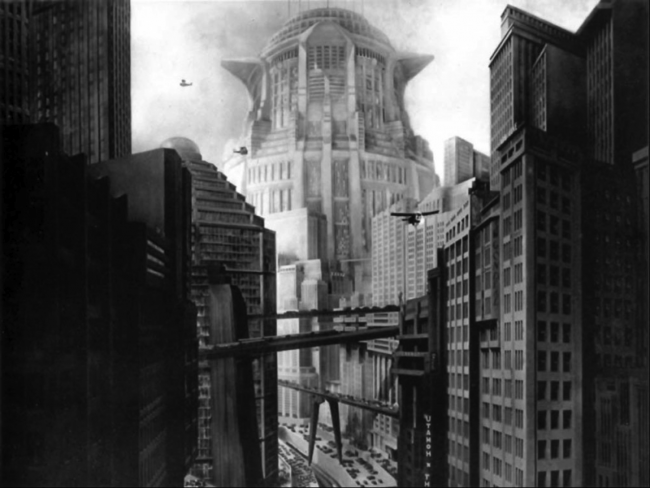 In this case the film Play Time by Jacques Tati in 1967 criticizes modern architecture as the hard way to the future as an ordered grid space.
In this case the film Play Time by Jacques Tati in 1967 criticizes modern architecture as the hard way to the future as an ordered grid space.
Architecture for the future and future concepts of living
Another idea related to the future is the architecture designed for eternity, to remember something or someone. Is designed to pass on to posterity, not to solve a problem in the future but to be a landmark.

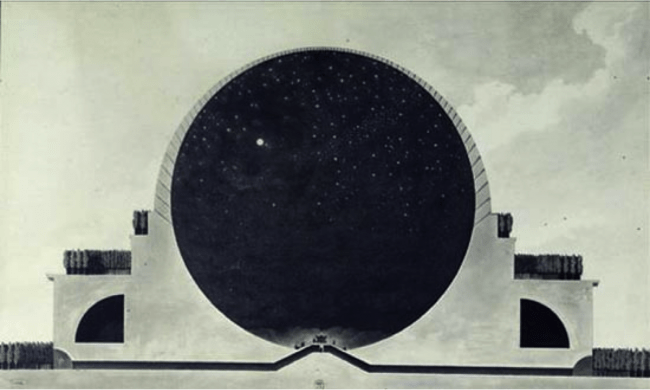 In other way, when Le Corbusier wrote towards an architecture he was thinking in the future time we are going toward. Modernism designed to meet the needs of modern life. to resolv the new needs and the confort of a man with a new spirit. A spirit for the future.
In other way, when Le Corbusier wrote towards an architecture he was thinking in the future time we are going toward. Modernism designed to meet the needs of modern life. to resolv the new needs and the confort of a man with a new spirit. A spirit for the future.
 In 1956 Alison and Peter Smithson designed a house to the future. The house was conceived using plastic, and has a courtyard in the middle. Attracts attention that all the geometry used in the plan are organic shapes.
In 1956 Alison and Peter Smithson designed a house to the future. The house was conceived using plastic, and has a courtyard in the middle. Attracts attention that all the geometry used in the plan are organic shapes.
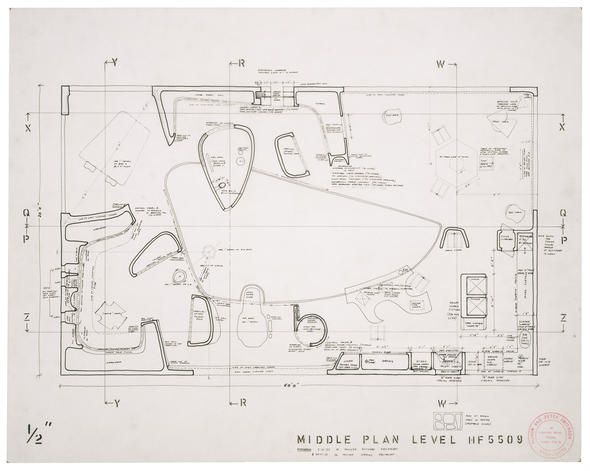 Nowdays A cartoon serie invent a corporatios thar made houses in capsules that are able to grow. It colud be fantasious an utopic baut nowadays this ideas are under reserching. Fostes and Partnes are working on the idea of to built on the moon using on site materials. a concept that might seem naive but is currently on the market and under investigation. They used a machine to be able to manufacture the necessary parts from the lunar material itself .Was this an experiment, a fantasy or an utopic idea?
Nowdays A cartoon serie invent a corporatios thar made houses in capsules that are able to grow. It colud be fantasious an utopic baut nowadays this ideas are under reserching. Fostes and Partnes are working on the idea of to built on the moon using on site materials. a concept that might seem naive but is currently on the market and under investigation. They used a machine to be able to manufacture the necessary parts from the lunar material itself .Was this an experiment, a fantasy or an utopic idea?
In other way foster and partners are with European Space Agency to built structures on the moonusing 3d printers.
 the structures would be useful to cover a refuge and to be buried with sand for protection from meteorites, gamma radiation and high temperature fluctuations
the structures would be useful to cover a refuge and to be buried with sand for protection from meteorites, gamma radiation and high temperature fluctuations
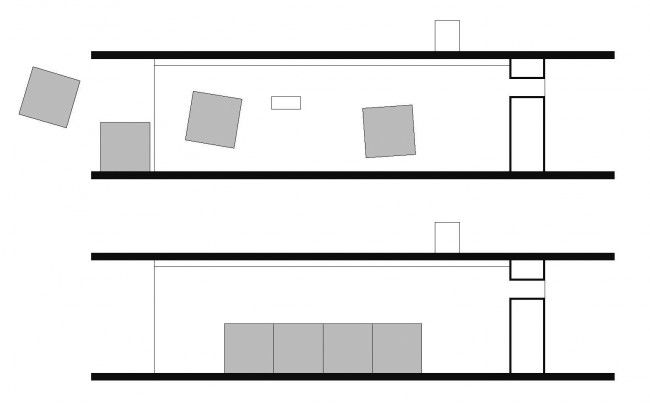
Flexibility is another concept whichu can resolv a lot of problmes. Diaphanous space adapt a lot of ways of living. Neked House by Sigeru Ban is a radical example of this concep. In this house rooms can move to set another configuration of space.
A diaphanous (daiafanous) space in which movable rooms are inserted
 The future of the cities: Smart Cities.
The future of the cities: Smart Cities.
Some of the examples considered have been:
Integration into “smart cities” sharing resources and infrastructures of the future city. This will require both urban and technological analysis, studying the consequences of its implementation both in improving the quality of future public space and its impact in systems based on new technologies of monitoring and automation of homes. The city will be conceived; interconnecting (Leisure, jobs and housing), resolving the resources, solving the circulations, Regulating itself, Sharing resources and being more efficient energyzed.
In the sixties, the british avand-garde architectural group Archigram proposed several experimental projecs as: Plug-in city, the walking city or the instand city. Paralelly, metabolist japanesse experimented about the future of the cities, they suggested the city as clusters interconnected
 How we will live in one hundred years?
How we will live in one hundred years?





























